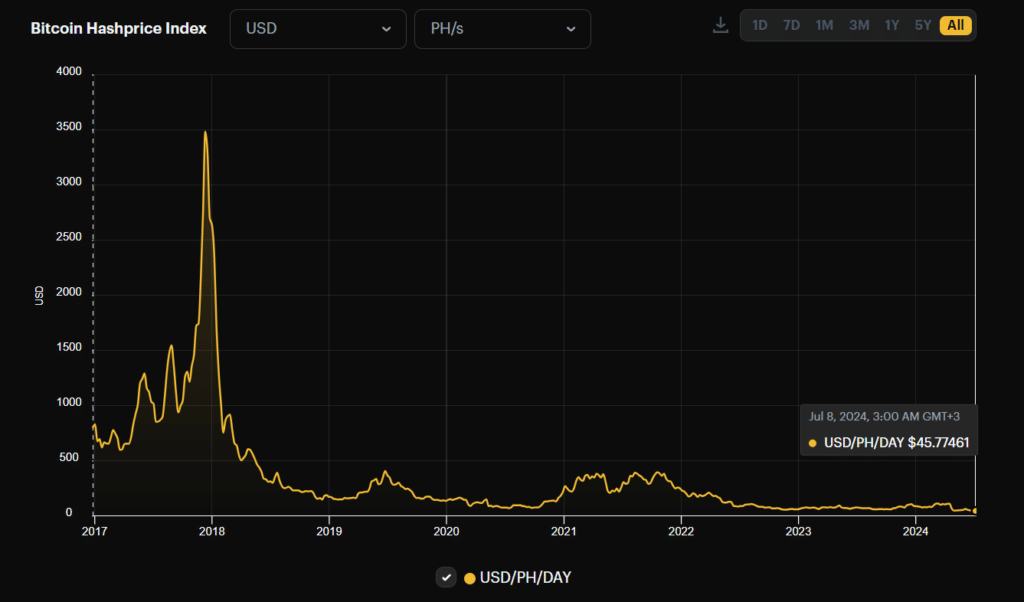
As a researcher with extensive experience in crypto markets, I find last week’s Bitcoin price drop and subsequent hashprice plunge deeply concerning. The all-time low hashprice of $44.31 per petahash per day (PH/day) is a stark reminder of the disruptions caused by China’s 2021 mining ban, which saw similar declines in miner revenue.
Last week, the decrease in Bitcoin‘s value, intensified by German financial transactions, caused hashrate price to reach a record low of $44.31 per terahash per day. This occurrence came about even with a 5% reduction in mining difficulty.
The recent decline in Bitcoin’s (BTC) price last week, exacerbated by German government sell-offs, led hashprice – a measure indicative of miner revenue per terahash – to reach an record low. This situation brought back recollections of the summer of 2021 when China enforced its Bitcoin mining ban, causing significant disruptions within the crypto’s mining community.
According to Hashrate Index’s latest data, last week saw a significant drop in hashprice to $44.31 per petahash per day (PH/day), marking the lowest metric observed in the crypto market thus far. In comparison, during May 2021 when Chinese authorities enforced strict regulations on crypto mining and trading, hashprice only declined from 379 PH/day to 203 PH/day.
The costs for conducting transactions on the Bitcoin network have significantly decreased, hitting a record low last seen during the third quarter of 2023 in terms of transaction volume.
As a crypto investor, I’ve noticed that the transaction fees on the Bitcoin network reached a nine-month low on July 8, according to Colin Harper, the head of research at Luxor Technology. Specifically, only 12.32 BTC in transaction fees were processed that day. This is the lowest level since October, 2023, when fees amounted to just 11.4 BTC. Coincidentally, Bitcoin experienced a significant price surge of 28.5% around that time.
In the third quarter of 2024, Bitcoin’s hashrate is expected to undergo frequent adjustments due to the ongoing struggle between three primary factors: the implementation of heat-related restrictions, the volatile pricing of hashpower, and the deployment of advanced ASICs by miners.
Colin Harper
The current sequence of three successive decreases in difficulty adjustments recalls the volatile summer of 2021, when Bitcoin experienced considerable turmoil due to China’s clampdown on mining and trading activities. In contrast, this year’s downturn comes after a tumultuous post-halving period during which Bitcoin’s hashrate dropped by approximately 10%.
Read More
- Silver Rate Forecast
- Grimguard Tactics tier list – Ranking the main classes
- USD CNY PREDICTION
- Gold Rate Forecast
- Former SNL Star Reveals Surprising Comeback After 24 Years
- 10 Most Anticipated Anime of 2025
- Black Myth: Wukong minimum & recommended system requirements for PC
- Box Office: ‘Jurassic World Rebirth’ Stomping to $127M U.S. Bow, North of $250M Million Globally
- Hero Tale best builds – One for melee, one for ranged characters
- Mech Vs Aliens codes – Currently active promos (June 2025)
2024-07-09 10:00