As a seasoned analyst with over two decades of experience observing the evolution of technology and finance, I find DePIN to be a fascinating development that bridges the gap between the digital and physical worlds. With my background in both fields, I have seen firsthand how traditional infrastructure can benefit from blockchain’s transparency and efficiency.
What exactly is DePIN, and how does it function, as it brings the chance for developing DeFi projects that compensate real-world actions? Essentially, this technology enables users to create decentralized finance projects that reward activities outside of the digital realm.
Table of Contents
Predictions from theoretical studies about cryptocurrencies suggest that encryption tools used in blockchain technology will eventually be applied to the internet and influence the real world in some way or another. As early as the end of the 20th century, Nick Szabo foresaw smart contracts being able to autonomously manage physical items. Now, over two and a half decades later, the blockchain has become an integral part of our daily lives.
This predominantly stems from the rise of cryptocurrencies, with Bitcoin (BTC) consistently setting new highs and backed by substantial real-world infrastructure. At a casual observation, it seems to indicate a tangible existence in our reality.
On the other hand, the frontiers of decentralized technologies are broadening as innovative solutions like DePIN emerge.
What is DePIN and why does blockchain need it?
A DePIN (Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network) is essentially a system where participants in the blockchain collaborate to create and manage actual world infrastructure projects by employing a public ledger and cryptocurrency. To put it simply, DePIN operates by utilizing a decentralized blockchain network to run and maintain networks of equipment that can collectively serve a particular purpose.
As a researcher, I’m exploring ways to construct networks in a manner that deviates from the traditional hierarchical approach commonly used in large-scale infrastructure projects like bridges and roads. Instead, I aim to establish these networks on decentralized, horizontal connections. This method is chosen because it offers advantages over the conventional hierarchical model, particularly in terms of cost efficiency and complexity. Given the high costs and intricacies involved in building and managing physical infrastructure networks, they have traditionally been the realm of large corporations or governments with substantial resources at their disposal.
Instead of being mandatory, DePIN promotes voluntary collaboration among its participants. Individuals can engage with DePIN networks by leveraging their personal equipment or acquiring specialized tools designed for specific tasks. Ranging from basic hard drives to weather stations, these options cater to various levels of participation. Generally, DePINs are structured around technologies that are accessible to the general public.
Max Thake, a co-founder of peaq, shared with crypto.news that DePIN motivates individuals by utilizing tokens as rewards for employing linked hardware to provide services to others.
Picture a decentralized network service similar to Roam Network, but with a focus on smartphones. The users’ smartphones serve as the hardware infrastructure, while the data they collect about local connection quality acts as the commodity. Telecom companies seeking to enhance their services purchase this data through a Web3 marketplace. Smart contracts facilitate this transaction, ensuring seamless value exchange between suppliers and buyers.
Max Thake, co-founder of peaq
What are the DePIN options?
There are two types of DePINs: Physical Resource Networks (PRN) and Digital Resource Networks (DRN).
In simpler terms, PRNs, or Peer-to-Peer Resource Networks, are decentralized systems where providers offer hardware assets (like sensors or internet connections) that are associated with a particular location. Since their contribution to the network relies on their specific location, these resources cannot be swapped or exchanged with others.
In DRNs (Distributed Resource Networks), service providers offer resources based on their functionality, rather than their geographical location. This means that the physical location of a resource is irrelevant in this context. Resources could include processing capabilities, data transfer speeds (bandwidth), or storage space.
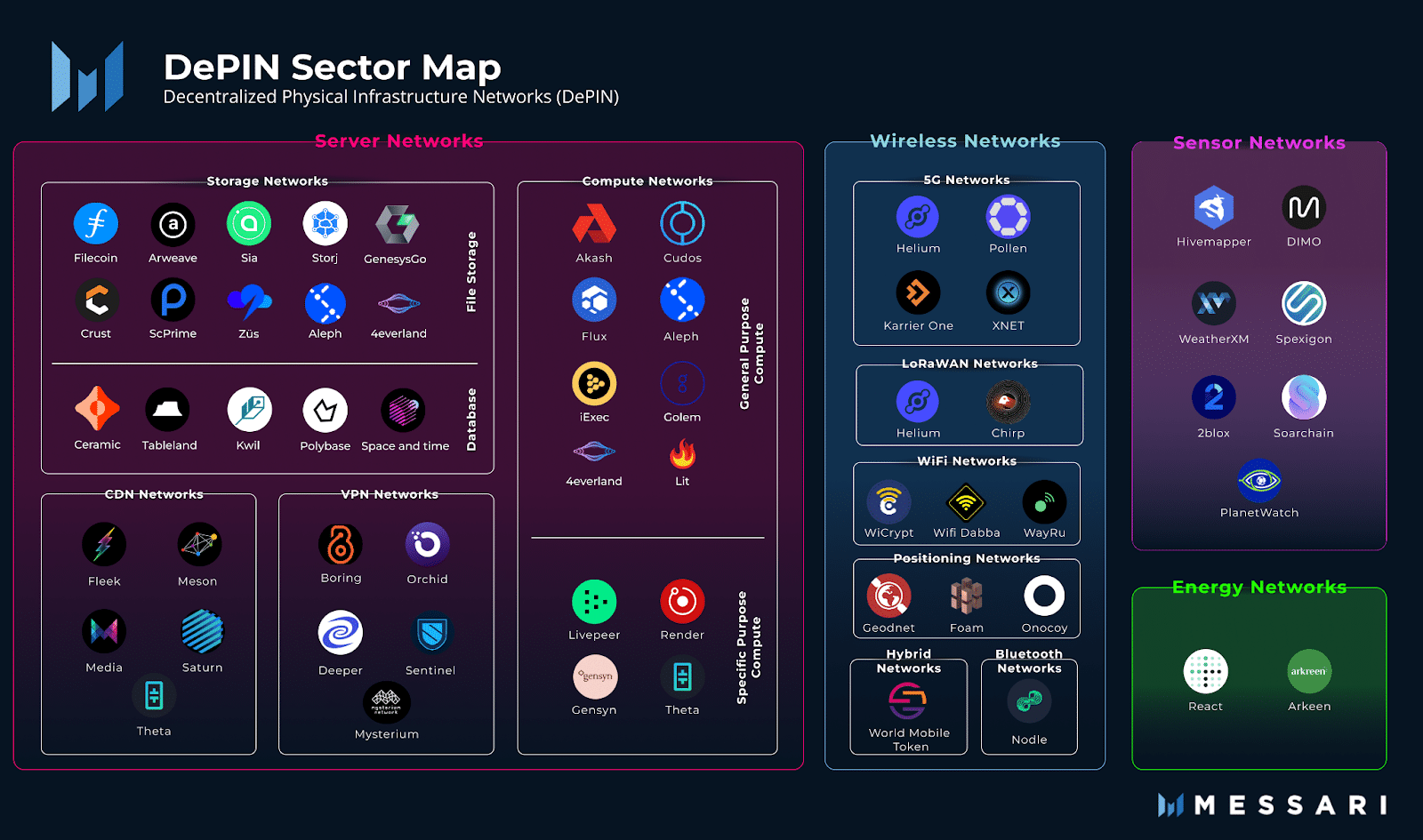
Advantages and disadvantages of DePIN
The DePIN system, conceptually, could revolutionize our approach towards managing and engaging with physical infrastructures. By leveraging blockchain technology and smart contracts, it enhances the productivity and openness of these systems, empowering the community to make self-governing decisions.
DePIN might be seen as an “industrial version of a DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization),” where every participant enjoys equal chances and contributes to the autonomy of the infrastructure. This system is adaptable, capable of expanding horizontally. By effectively drawing in enthusiastic users, the construction of a decentralized physical infrastructure can be notably expedited.
In the decentralized cryptocurrency system known as DePIN, the pricing model stands out for being more open and equitable. This is because the essential infrastructure assets are collectively owned by the community, rather than a single company. The cost of services isn’t dictated by corporate profits but by availability instead. By distributing tokens to participants, users can earn a consistent passive income, thereby contributing to societal benefits.
However, significant disadvantages should be considered:
- Vulnerability to hacks and errors.
- High volatility of tokens.
- There is a need for technical knowledge to maintain a decentralized infrastructure.
Despite the fact that other systems might exist, DePIN’s use of blockchain technology enables its application in real-life scenarios and value transfers. This connection to the real-world supply and demand dynamics gives this sector a distinctive advantage when it comes to long-term, robust expansion.
Individuals continue to utilize navigation tools, order food online, and browse the web regardless of Bitcoin’s price fluctuations. DepIN, however, combines the elements of web3 with tangible value rather than speculation, providing an opportunity for it to truly fulfill its potential of transforming the world.
Looking to the future: What will happen to DePIN in five years?
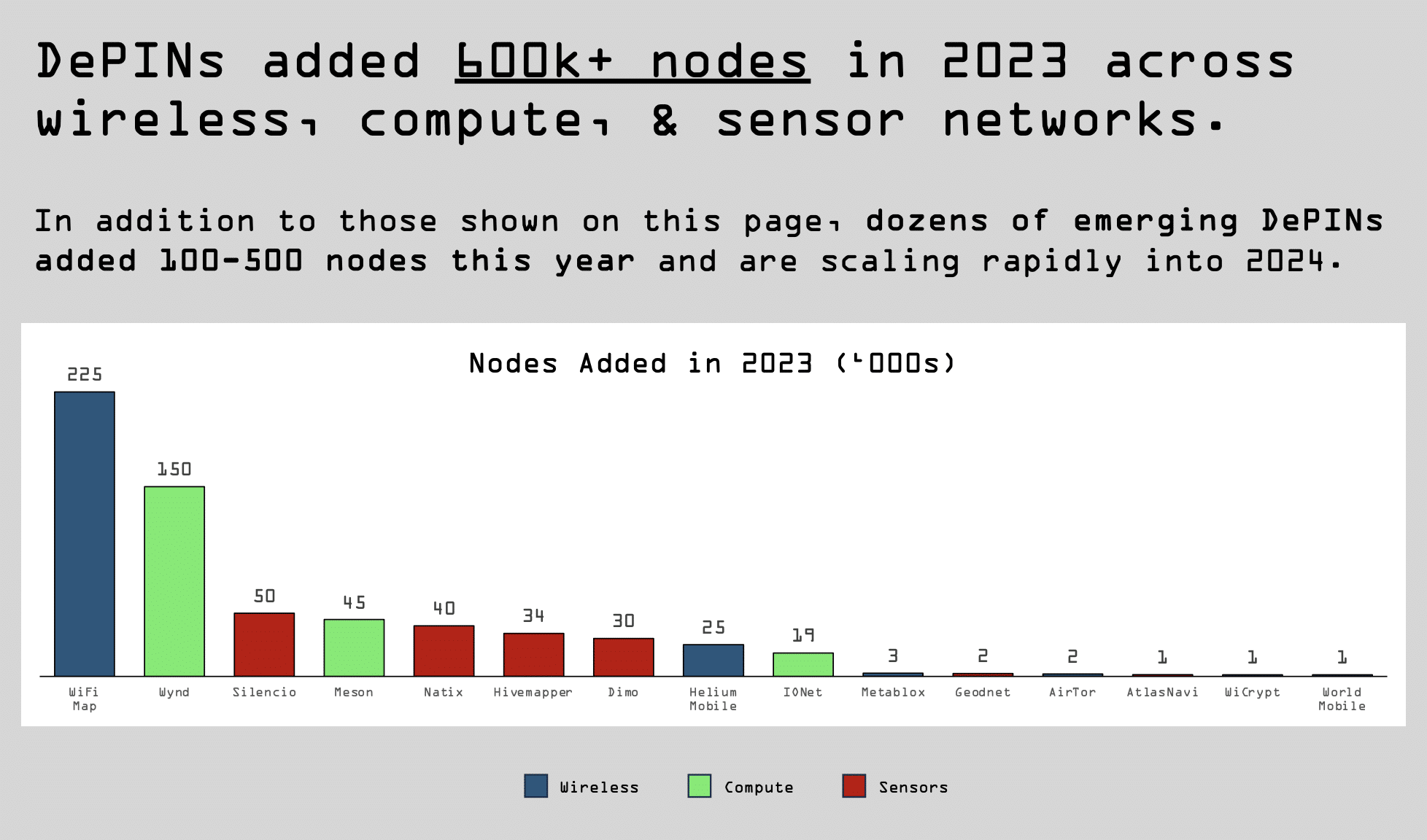
As per Messari analysts’ findings, by 2023, the DePIN ecosystem expanded to over 650 projects and witnessed a significant growth of approximately 600,000 nodes. The researchers highlighted key trends expected in the development of DePIN throughout 2024.
As a researcher delving into the realm of blockchain technology, I am optimistic about the role meme tokens could play in fostering widespread adoption of projects such as the BONK airdrop for Solana Saga smartphone users. Furthermore, analysts predict that Asia will be the region where the growth of decentralized infrastructure is most rapid. It’s anticipated that some of the sector’s most impactful projects will emerge in this region between 2024 and 2025.
Approximately a decade back marked the inception of advancements in the DePIN field. Since then, there’s been a substantial growth in the number of associated projects. Experts from Messari estimate that the sector’s market capitalization exceeds $20 billion, not including resources for risk-weighted assets (RWA) and blockchain oracles.
In conversation about the future of DePIN, Thake anticipates that it will establish itself as a standard in the industry, encompassing the full suite of supporting solutions. This includes data sourced collectively through DePIN for training machine learning models, decentralized computing, and marketplaces for AI agents based on Web3 federated learning.
Innovative applications of the DePIN model are likely to emerge in the energy sector, particularly in the realm of renewable or green energy. This is because flexible and distributed grid systems are essential for green energy, a contrast to the traditional centralized models. In the near future, individuals may generate income by harnessing solar power and feeding it back into the grid.
Despite not yet being widely recognized, even within the cryptocurrency community, DePIN projects remain relatively unknown. The implementation of decentralized infrastructure may require time due to challenges that need to be addressed. However, experts are optimistic about its potential impact on shaping the future and transforming the underlying principles of traditional physical infrastructure.
Read More
- USD MXN PREDICTION
- 10 Most Anticipated Anime of 2025
- Pi Network (PI) Price Prediction for 2025
- Silver Rate Forecast
- How to Watch 2025 NBA Draft Live Online Without Cable
- USD CNY PREDICTION
- USD JPY PREDICTION
- Brent Oil Forecast
- Gold Rate Forecast
- PUBG Mobile heads back to Riyadh for EWC 2025
2024-12-27 01:14