What exactly is surveillance capitalism, and why should you be worried about your online footprint?
Table of Contents
In our modern world dominated by technology, your private information holds significant value, being the foundation of what’s known as “surveillance capitalism” according to scholar Shoshana Zuboff at Harvard.
The omnipresent Surveillance Capitalism devoured the world, leaving democracy powerless to shield us from harmful digital practices. Our kids serve as vulnerable test subjects in the dangerous mines of digital technology, exposed to unwanted surveillance, addictive designs, manipulative dark patterns, and behavior-altering techniques. It’s time for change.
— Shoshana Zuboff (@shoshanazuboff) August 26, 2022
In simpler terms, Surveillance capitalism refers to a business strategy used by tech companies where they collect and analyze people’s data to anticipate and manipulate their actions, mainly for generating income from targeted advertisements.
How does surveillance capitalism function, though? In this system, your searches, clicks, “likes,” and lengthy gazes at the screen are all important pieces of data that are gathered, scrutinized, and then marketed to advertisers and other entities.
Companies such as Facebook and Google provide frequently used services for us. Functioning as data centers, they gather an enormous amount of information regarding our behaviors and inclinations.
With this information, we construct comprehensive portraits capable of anticipating and potentially shaping our choices and actions, typically sans our explicit approval.
This model has thrived during the digital era. For example, in the year 2023, the digital advertising sector, which places significant emphasis on user information, generated a worldwide revenue of more than $602 billion and is anticipated to grow up to $965 billion by the year 2028.
For businesses on a larger scale, what are the perks of engagement in surveillance capitalism? This model enables them to customize user encounters meticulously and optimize their services accordingly. Such improvements can lead to increased customer satisfaction and higher revenues.
With the increasing development of industries, there is a trend towards gathering larger and more detailed data. However, this growth brings up important ethical and privacy issues. Based on a 2019 Pew Research Center study, around 81% of Americans believe they have minimal influence over the information that businesses collect about them.
In search of solutions to these pressing concerns, blockchain emerges as a promising alternative.
A blockchain functions with decentralization and transparency at its core. In this system, transactions are encoded and authenticated by multiple network members, eliminating the need for individuals to share their private identities during the verification process.
This design not only improves users’ privacy but also prevents any individual from collecting and profiting extensively from large amounts of user data.
We can delve into the inner workings of surveillance capitalism and discuss potential solutions that crypto and blockchain tech offer in counteracting its impact.
Surveillance capitalism explained
Surveillance capitalism has fundamentally transformed how companies interact with consumer data.
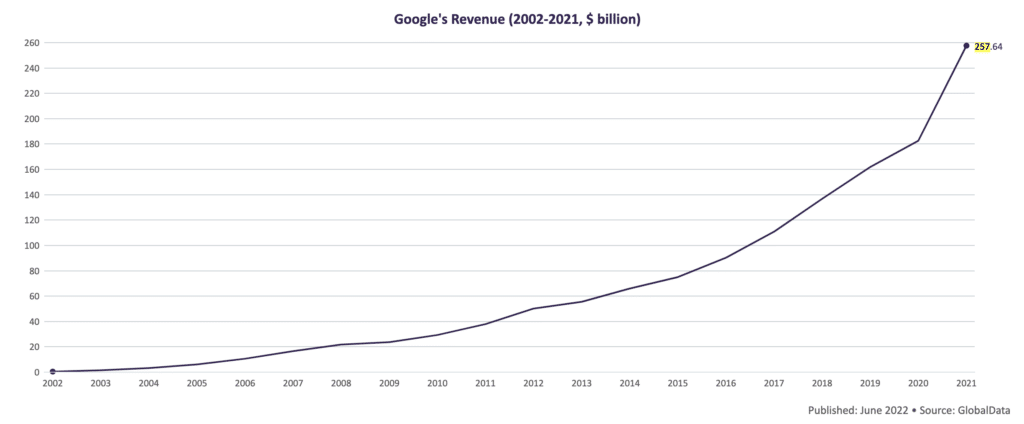
Google makes money by gathering extensive user data, such as search queries and YouTube choices, then using this information to offer customized ad placements for businesses seeking specific audiences.
In 2018, an AP investigation uncovered the fact that Google continues to gather location information from mobile devices, despite users disabling the Location History feature.
In the year 2021, advertising brought around 257.63 billion dollars, which represented about 81%, to Alphabet’s (the company that owns Google) overall earnings.
Just like Facebook uses its strong connection to users’ social worlds to customize ads.
Last year, 2021, Facebook earned approximately $114 billion through advertising, marking a significant increase from the $84 billion made in 2020. This growth underscores the substantial financial worth of users’ personal information.
Surveillance capitalism examples
In simpler terms, The Markup uncovered a disturbing situation in 2023 where the Meta Pixel tracking tool was discovered on several prominent American hospital sites.
This tool gathered personal health data such as medical history, medications, and doctor visits, then forwarded it directly to Facebook.
Thirty-three out of the hundred leading hospitals that were inspected found that clicking the “schedule an appointment” button transmitted a data packet to Facebook, which included the user’s IP address and potentially sensitive health information, without obtaining prior authorization from the patients.
Approximately one-third of frequently visited websites integrate Facebook pixels, according to The Markup’s real-time privacy tool, Blacklight. In a 2018 hearing before Congress, Facebook admitted that their pixels were present on over two million sites.
The Cambridge Analytica incident is a well-known cautionary tale about the potential dangers of surveillance capitalism. It came to light that Facebook granted access, without users’ approval, to the data of countless millions of its platform’s members. This information was subsequently employed to manipulate voter attitudes during the 2016 United States presidential election.
Other firms, like Amazon and Apple, also engage in forms of surveillance capitalism.
Amazon employs client information not only for enhancing sales of merchandise but also to manage markets and price lower than rivals, an approach subjected to investigation in a 2021 report by the US House Judiciary Committee.
Although Apple emphasizes user privacy in its promotions, it gathers substantial user data via Siri and iCloud. This information is then utilized to refine user profiles, enabling targeted advertisements within Apple’s platform.
The implications of surveillance capitalism extend beyond just targeted advertising.
Collecting, storing, and using data in this manner can create significant privacy dilemmas, as people may be unaware of the full scope of the information being gathered from them.
In addition, collecting and examining people’s information has wider implications for society, impacting areas such as credit scores and employment prospects, often without clear supervision or the ability for individuals to challenge mistakes.
Under surveillance capitalism, companies make money from collecting and using individuals’ personal data. This practice raises concerns not just for privacy, but also ethically, as it shifts the power dynamic between consumers and corporations.
Users are frequently faced with a dilemma: to utilize necessary services or safeguard their personal data, which questions the essence of informed consent.
Then, what’s the solution?
Can crypto really help avoid surveillance?
In simpler terms, crypto technology provides an unique method for protecting information that sets it apart from conventional financial structures.
In the crypto world, where transactions are based on blockchain technology, personally identifiable information like names and addresses aren’t necessary by default. This feature boosts users’ privacy and anonymity.
Bitcoins (BTC) and other cryptocurrencies protect user identities through the use of public key encryption. Every user is assigned a publicly accessible address on the blockchain, while their real identity stays hidden.
Using this approach, companies are limited in creating detailed consumer spending profiles, a frequent occurrence in surveillance capitalism.
Based on a study published in 2021, blockchain technology prevents third parties from commercially exploiting personal information without prior consent – marking a significant departure from the prevailing practices of data harvesting in the surveillance economy.
Additionally, cryptocurrencies offer opportunities to develop alternative economic structures, free from relying on ad revenues and the manipulation of user information.
Using blockchain technology, content creators have the ability to receive cryptocurrency payments directly from consumers without relying on intrusive advertising and the collection of extensive personal data for revenue.
An intriguing alternative is provided by crypto-driven platforms such as the Brave browser. Instead of using traditional money, Brave employs its own digital currency, called Basic Attention Tokens (BAT), to compensate users for their engagement with ads.
Using an opt-in method not only values user privacy but also shifts the advertising paradigm, providing compensation directly to viewers instead of leveraging their data for negotiations.
Based on data from Brave’s user growth report, the number of active users on their browser surpassed 50 million by the beginning of 2021. By April 2023, this figure had significantly increased to more than 172 million.
However, regulatory hurdles continue to impact the broader acceptance and use of crypto.
In simple terms, the regulatory attitudes towards cryptocurrencies differ significantly among various nations. For instance, countries including China have forbidden their usage entirely, while progressive nations such as El Salvador have incorporated them into their financial structures, subject to specific regulations.
These obstacles not only make it harder for users to access crypto but also restrict its ability to expand as a popular alternative to fighting surveillance capitalism.
Real-world applications and future outlook
Current implementations
Future potential
“The role of blockchain and cryptocurrencies in countering surveillance capitalism’s future is showing some exciting advancements.”
- Adoption of privacy coins: Increased use of privacy-focused cryptocurrencies could shift how personal data is handled, moving away from traditional data-exploitation models.
- Blockchain in consumer data rights: New blockchain projects may allow people to own and monetize their data. For instance, the Ocean Protocol provides a marketplace for secure, transparent data trading, ensuring users are compensated.
- Regulation and standardization: Clearer regulations could support the growth of crypto and blockchain, making them safer and more reliable for users.
- Integration with IoT: Blockchain’s role in the Internet of Things (IoT) is expanding. It could help secure vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices, from fitness trackers to smart home systems, ensuring this information is used ethically.
The future of crypto and surveillance
Anticipate a more profound adoption of blockchain technology in diverse fields, transcending monetary exchanges and touching upon areas such as healthcare, digital identification, and administration.
Using a blockchain can limit the power of any individual to misuse personal information, as it provides a barrier against such actions.
Additionally, with the growing concern over data privacy due to prominent data leaks and monitoring controversies, there may be a significant rise in consumers seeking tools that provide more autonomy and clarity.
Although the journey ahead is not free of challenges, regulatory guidelines must adapt to foster crypto development and safeguard users simultaneously.
Another important consideration is enhancing blockchain technology’s ability to handle larger scales to cater to worldwide adoption.
With every advancement in blockchain and cryptocurrency technology, we get nearer to a more equitable and safer digital realm.
Read More
- USD MXN PREDICTION
- 10 Most Anticipated Anime of 2025
- Pi Network (PI) Price Prediction for 2025
- Silver Rate Forecast
- USD JPY PREDICTION
- How to Watch 2025 NBA Draft Live Online Without Cable
- USD CNY PREDICTION
- Brent Oil Forecast
- Gold Rate Forecast
- PUBG Mobile heads back to Riyadh for EWC 2025
2024-04-19 17:10